Exercises with the DualMCU Board - MicroPython
5. Control Servo
Objective
Utilize the DualMCU board with RP2040 to control a servo motor, enabling movement to specific angles. This includes the capability to manage the servo within a defined range or allow predefined sequences of movement.
NOTE In this practices, you will use the microcontroller RP2040.
Descriptions
This section demonstrates a combination of resources and code design for controlling servo motors using MicroPython. Servo motors play a crucial role in robotics and automation projects, providing precise control over the positioning of axes. With MicroPython, it becomes easy to create a simple and efficient interface for the effective control of servo motors, empowering users to easily incorporate this component into their projects.
Materials
Conection Diagrams
To continue, this section presents a connection diagram, which is straightforward. You only need to connect the DualMCU board to the servo motor according to the diagram and load effective control of the servo motor.
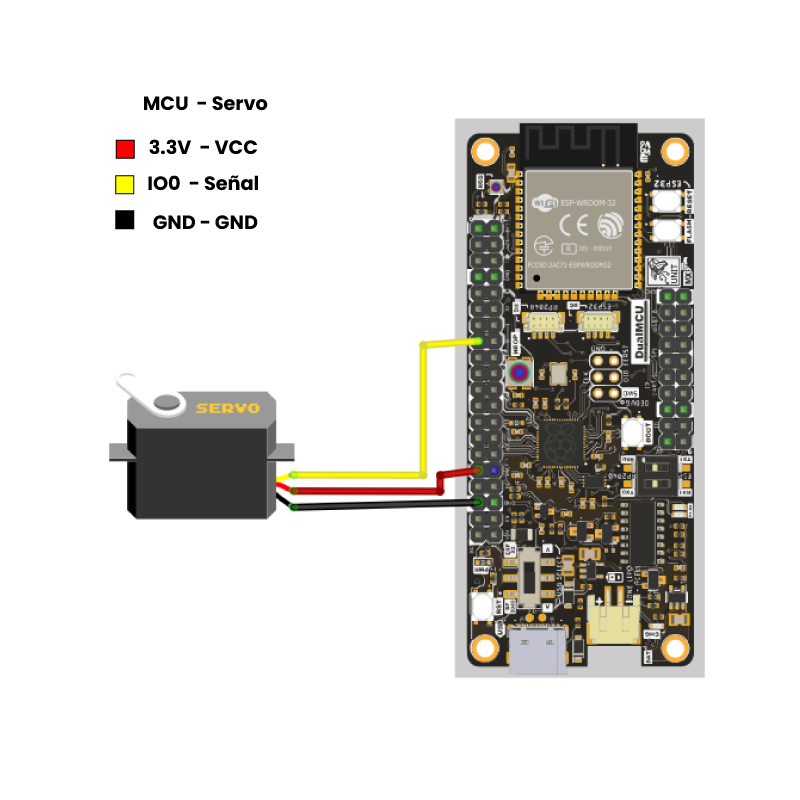
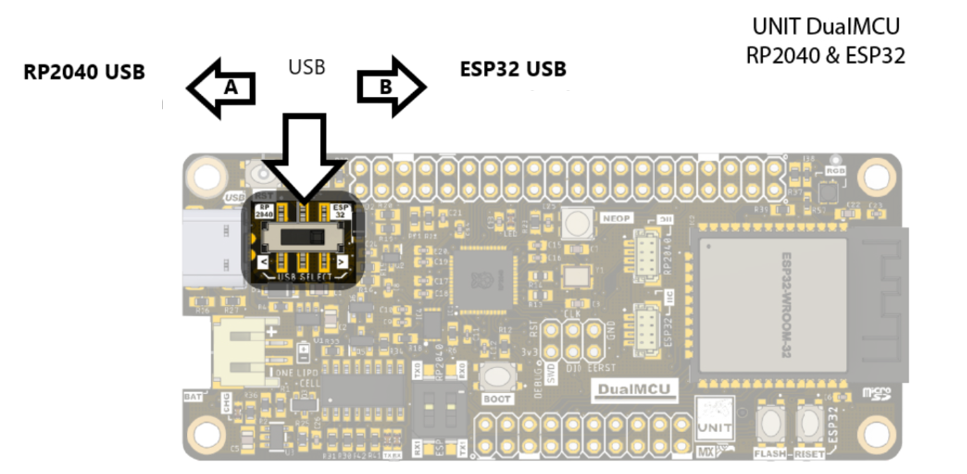
NOTE Remember that when working with the DualMCU board, you can interchange between microcontrollers using interrupt-driven changes. For these practices with the RP2040 microcontroller, make sure to switch the selector to position “A”.
Code
The code serves as an example for RP2040, configuring the output destined for the servo motor and controlling it using the GPIO 0 output.
'''
Unit Electronics 2023
(o_
(o_ //\
(/)_ V_/_
Tested Code Mark
Version: 0.0.1
Revision: 0.0.1
Test Code
'''
import machine
import utime
# PWM pin configuration
pwm_pin = machine.Pin(0) # Change to machine.Pin(1) if using GPIO pin 1
pwm = machine.PWM(pwm_pin)
# PWM frequency in Hz (adjust as needed)
pwm.freq(1000)
try:
while True:
# PWM duty cycle (0-65535, where 0 is off and 65535 is fully on)
for duty_cycle in range(0, 65536, 5000):
pwm.duty_u16(duty_cycle)
utime.sleep(0.1)
# Reverse the duty cycle for a fading effect
for duty_cycle in range(65535, -1, -5000):
pwm.duty_u16(duty_cycle)
utime.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# Stop PWM and clean up resources when program is interrupted with Ctrl+C
pwm.deinit()
print("\nPWM stopped. Resources released.")
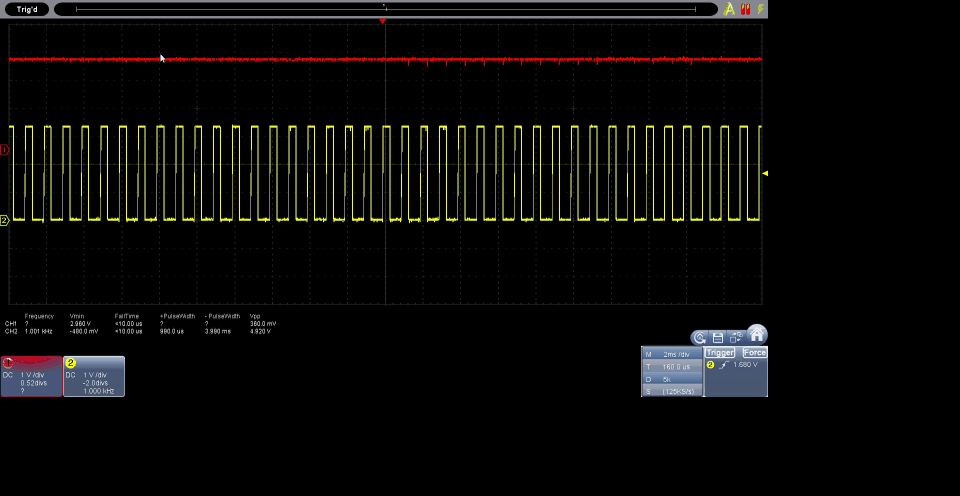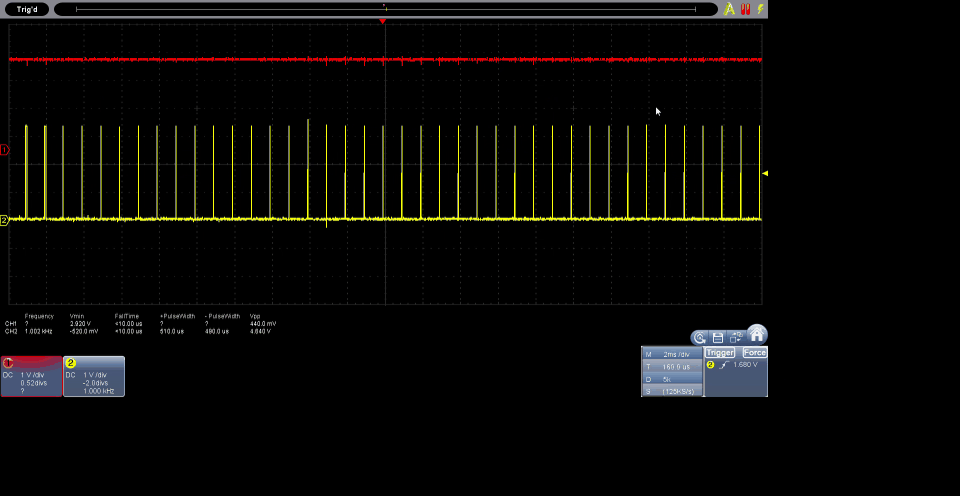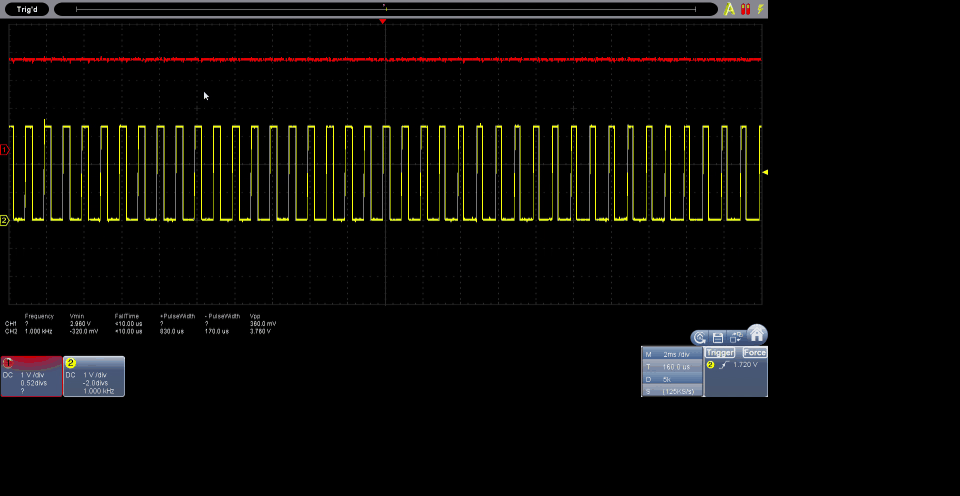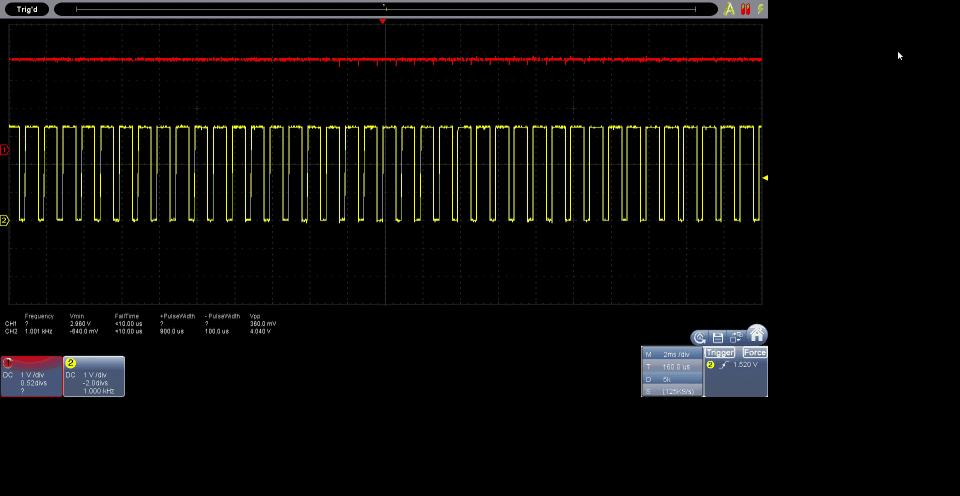
The code provides a solid foundation for controlling servo motors with RP2040 and can be easily adapted to the specific characteristics of other servo motors. The ability to configure parameters such as frequency and angles makes this code versatile and applicable to a variety of projects that require precise control of servo motors.
import machine
import utime
# Configuration of the servo motor control pin (you can change it according to your connections)
servo_pin = machine.Pin(0) # Change to your desired pin
# Create a PWM object to control the servo motor
pwm_servo = machine.PWM(servo_pin)
# PWM frequency for the servo motor (usually around 50 Hz)
pwm_servo.freq(50)
def set_servo_angle(angle):
# Convert the desired angle (in degrees) to a duty cycle value
# Note that specific values may vary depending on the servo
duty_cycle = int(1024 + (angle / 180) * 3072)
pwm_servo.duty_u16(duty_cycle)
try:
while True:
# Move the servo motor from 0 to 180 degrees
for angle in range(0, 181, 10):
set_servo_angle(angle)
utime.sleep(0.1)
# Move the servo motor from 180 to 0 degrees
for angle in range(180, -1, -10):
set_servo_angle(angle)
utime.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# Stop PWM and clean up resources when interrupting the program with Ctrl+C
pwm_servo.deinit()
print("\nPWM stopped. Resources released.")
The function set_servo_angle(angle) converts the given angle into a specific position (ranging from 0 to 180 degrees) suitable for the servo motor. Instead of running in an infinite loop, the code smoothly moves the servo motor from 0 to 180 degrees and vice versa, with a brief pause between each extreme position. The program can be interrupted using Ctrl + C. Upon termination, it stops the PWM and frees up resources.
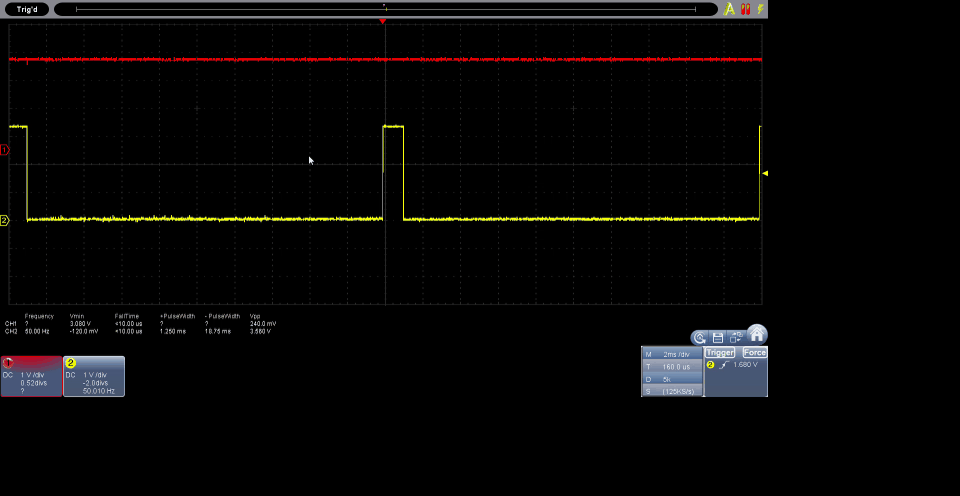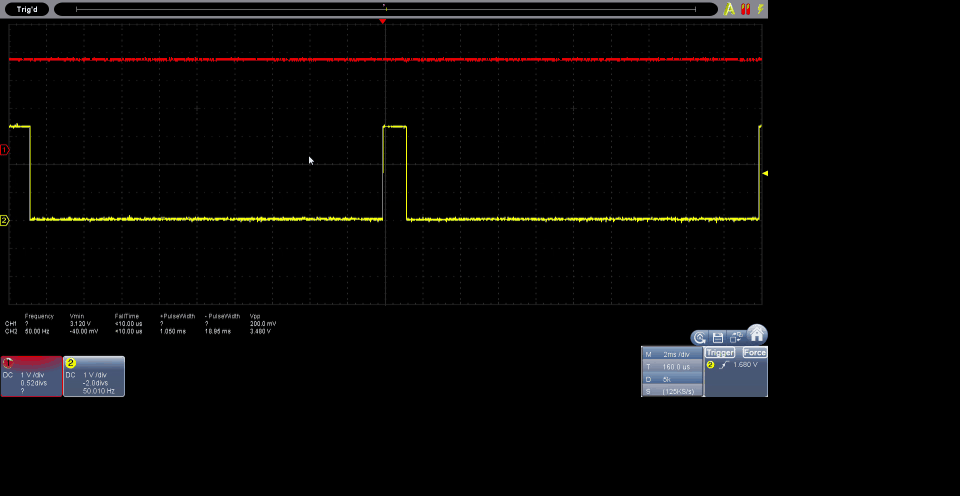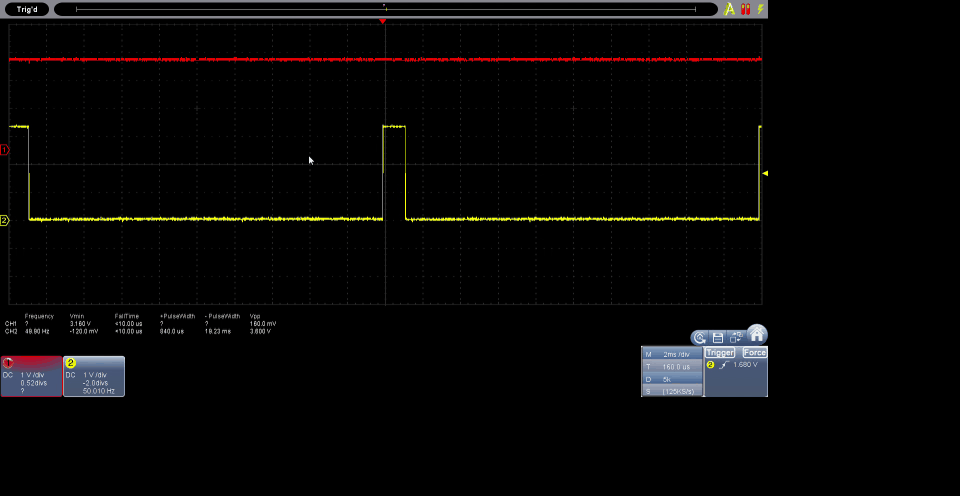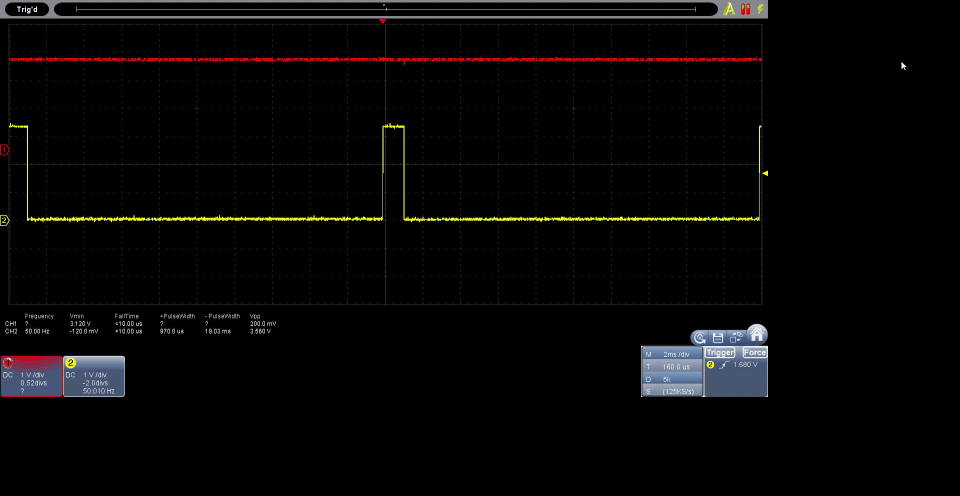
Results
The results obtained from the code implemented with MicroPython on the DualMCU board with RP2040 enable efficient control of the servo motor using pulse width modulation (PWM). The code utilizes GPIO 0 (as per connections), configures it into a PWM channel, and establishes a frequency of 50 Hz for servo motor control.
Conclusions
The practice involving the DualMCU board and a servo motor serves as an introductory experience in controlling a physical device using both microcontrollers. The RP2040’s demonstrated ability to manage control signals for servo motors provides a precise understanding of GPIO pins and PWM pulse generation for motor position and movement control.
This experience establishes a solid foundation for addressing more complex applications in device control, especially in robotics, automation, or embedded systems projects. The knowledge gained through this practice creates a platform for exploration and development of more advanced solutions, allowing users to enhance their skills in hardware control.
To further advance these skills, it is recommended to review and experiment with samples related to PWM in the DualMCU repository. This will facilitate a deeper understanding and practical application of the concepts learned in this practice.
NOTE: Keep in mind that the presented codes are only examples and may require configuration adjustments according to specific needs and requirements.
In order to enhance your skills, you can check the example related to PWM in the DualMCU repository
Continue with the course Alarm System
- License The code presented in this repository is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 3.0.
⌨️ with ❤️ from UNIT-Electronics 😊