Exercises with the DualMCU Board - MicroPython
3. Led Blinking
Objective
The main goal of this section is to develop the necessary skills to program a flashing effect, commonly known as “Blink” in programing, at a specific frequency.
NOTE: Utilize the two microcontrollers of board DualMCU.
Description
The implementation of a simple LED blinking program is supported by various beneficial purposes. Among them, it highlights the verification of the initial functionality of the DUALMCU, understanding the program structure for each microcontroller, familiarization with the programming environment, and the hardware associated with the DUALMCU. This initial exercise lays the essential foundations for successfully tackling subsequent activities.
The procedure to carry out this exercise involves the use of the two RGB LEDs integrated into the UNIT DUALMCU development board. The configuration and programming of both microcontrollers will be coordinated, allowing the desired blinking effect to be achieved. This exercise not only provides a practical introduction to LED handling and programming but also establishes a solid foundation for future practical activities in this specific development environment.
Materials
To carry out the program implementation, two RGB LEDs will be employed are fully integrated into the development board. Hereafter, the detailed specifics of the materials to be used in this activity are provided.
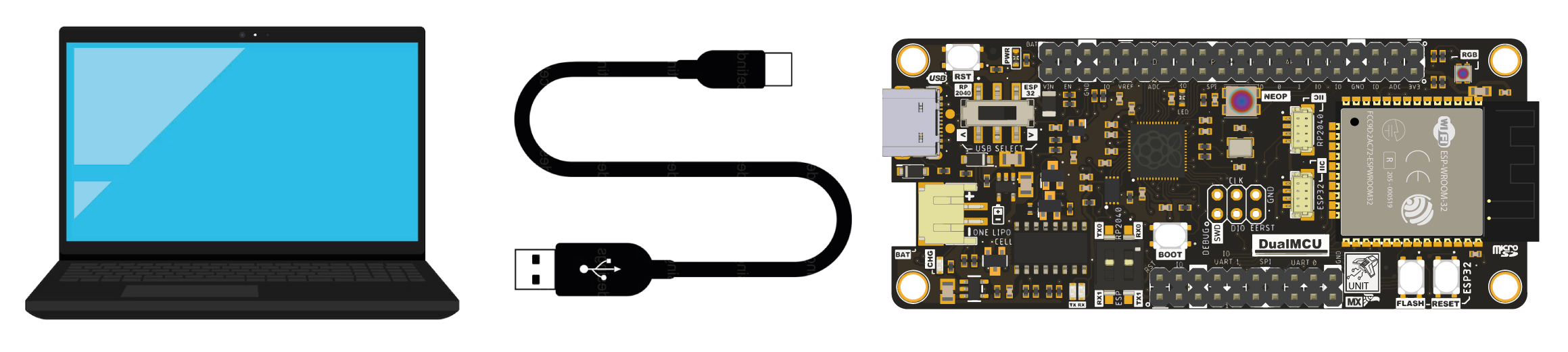
Connection Diagram
To proceed, simply connect the board DUALMCU to your laptop or desktop computer using a USB Type-C cable.
Software
After connecting the DUALMCU unit to the computer, proceed to turn on the device and select the desired microcontroller (MCU).

NOTE In case the DUALMCU board is not recognized, it will be necessary to install the CH340 driver. This driver is crucial for establishing communication and programming with the ESP32 microcontroller.
Code
Use the following code to verify the functionality of the MicroPython firmware installation. Ensure that the ESP32 microcontroller is selected, and load the following code.
'''
Unit Electronics 2023
(o_
(o_ //\
(/)_ V_/_
tested code mark
version: 0.0.1
revision: 0.0.1
'''
import machine
import time
led_pin = machine.Pin(4, machine.Pin.OUT)
led_pin2 = machine.Pin(26, machine.Pin.OUT)
led_pin3 = machine.Pin(25, machine.Pin.OUT)
def loop():
while True:
led_pin.on()
led_pin2.on()
led_pin3.on()
time.sleep(1)
led_pin.off()
led_pin2.off()
led_pin3.off()
time.sleep(1)
loop()
This code is intended to test the configuration of the installed MicroPython for ESP32. The code turns on the three LEDs and turns them off after a 1-second interval. You can adjust the frequency of the flashing LEDs by modifying the parameter in the time.sleep(1) function. For example, changing it to time.sleep(0.5) will make the LED flash every 0.5 seconds instead of 1 second.
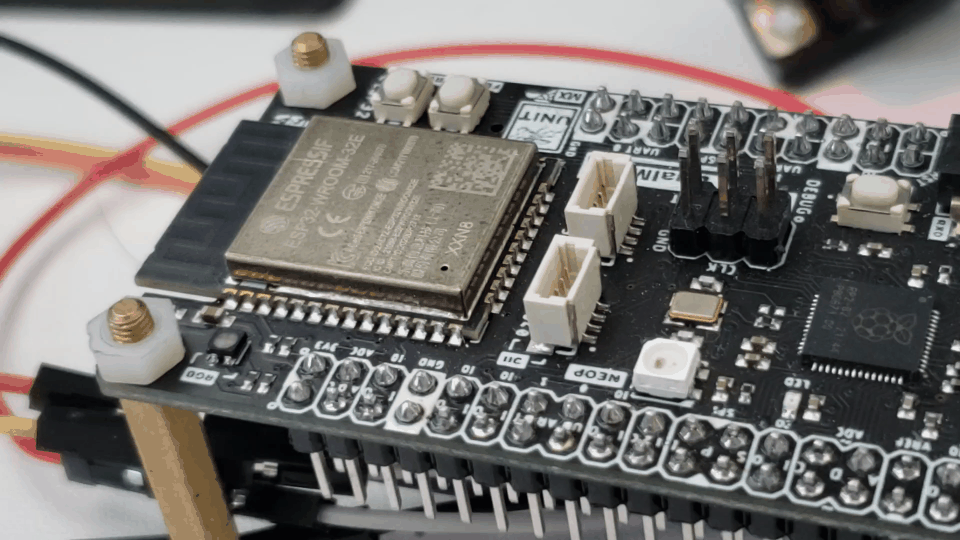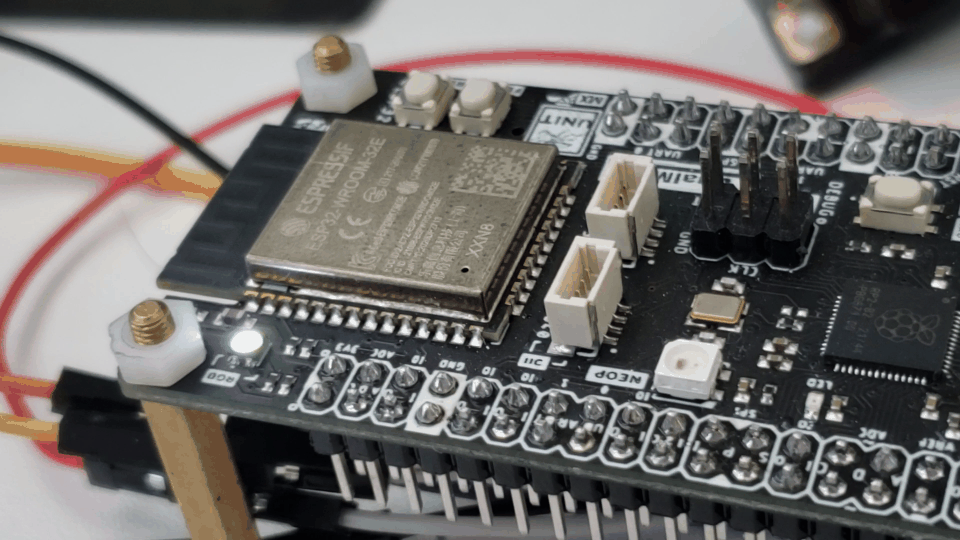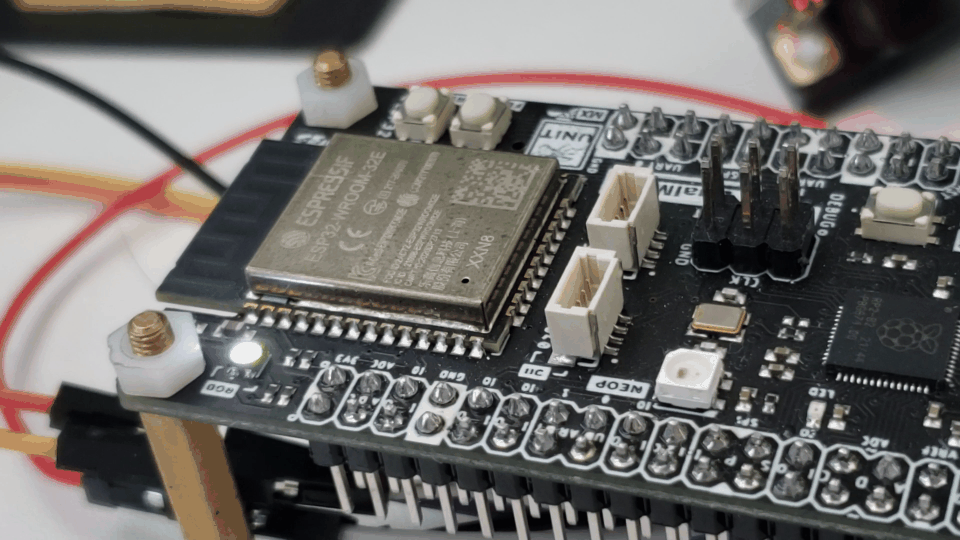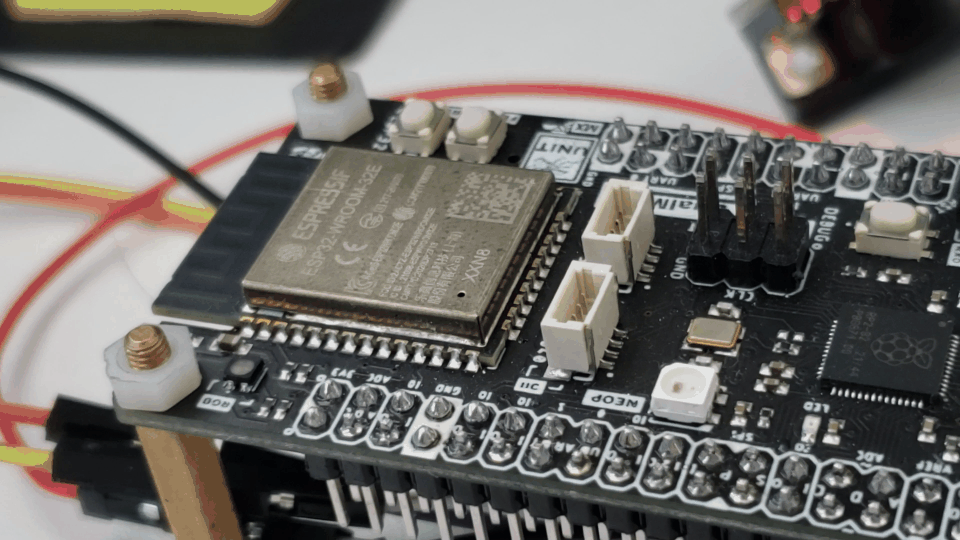
Results
Below is the function’s code demonstrated in the following gif:
Interaction with the RP2040
- Ensure that the selector is always set to the position designated for RP2040 on the DualMCU.
- Update the COM serial port, based on the operating system configuration.
- Open Thonny and copy the code.
- Paste the code and run it to observe the LED corresponding to the RP2040.
'''
Unit Electronics 2023
(o_
(o_ //\
(/)_ V_/_
'''
import machine
import utime
led = machine.Pin(25, machine.Pin.OUT) # Configura el pin GPIO25 como salida
while True:
led.value(not led.value()) # Invierte el estado del LED (encendido/apagado)
utime.sleep(1) # Espera 1 segundo
Conclusion
These LED flashing exercises on the DualMCU board not only serve as an introduction to programming the MCUs (RP2040 & ESP32) and managing the board using MicroPython but also provide a solid foundation for exploring and expanding your understanding and abilities. This will prepare you for the upcoming exercises in your future projects.
NOTE: Keep in mind that the presented codes are only examples and may require configuration adjustments according to specific needs and requirements.
Continue with the course Temperaure Sensor (ADC)
- License The code presented in this repository is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 3.0.
⌨️ with ❤️ from UNIT-Electronics 😊